As we have witnessed with recent financing activity for private biopharma companies, which saw 50 financings in excess of $100 million in the first half of 2024, a similar trend is emerging in life science M&A activity, which is experiencing a significant increase in the number of transactions exceeding $1 billion. As is noted in the illustration of deal activity from 2000 through the first half of 2024, for much of the period, deals of this size made up roughly 10% of announced transaction fairly consistently. However, beginning in the later part of 2023, acquisitions of $1 billion dollars plus rose markedly, accounting for a of transactions announced in the most recent quarter, more than three times the annual historical total. This trend may reflect an increased appetite for deals intended to “move the needle” more expeditiously, which may also be a key driver of the large private company financings. Perhaps additional evidence of a philosophical embrace of the "go big or go home" mantra.
0 Comments
In a recent sampling of biopharmaceutical companies we conducted, a stark contrast emerged between companies who had not yet filed an IND and those that had. We were astonished to discover that roughly 80% of companies without a drug in the clinic did not list a Chief Medical Officer among their executive leadership, while the reverse is true of clinical stage companies. Based on discussions with senior executives to understand this bifurcation in greater depth, it became apparent that many recognize the merits of aligning their intended clinical trial pathway with preclinical initiatives. These same companies, however, rely on key opinion leaders or their scientific advisory board members as a substitute for the expertise of a Chief Medical Officer.
This reliance is likely misguided and can contribute to protracted development timelines and escalating financial costs. KOLs and SAB members do play critical roles in guiding the advance of development programs, but their role is distinct from that of a Chief Medical Officer and the two roles are not interchangeable. KOLs and SAB members possess an extensive understanding of a specific disease state but not necessarily an intimate appreciation of the strategic and operational aspects of drug development. These capabilities fall squarely within the domain of the Chief Medical Officer. Particularly for earlier-stage private companies who do not need a full-time executive, accessing a Chief Medical Officer on a fractional or interim basis enables these companies to gain the significant benefit of this expertise without incurring the burden of a full-time hire. The Chief Medical Officer (CMO) is a core member of any biopharmaceutical company’s leadership team. This executive is responsible for the design and execution of a clinical development strategy that is central to the company’s success. As such, significant time and resources are committed to hiring a CMO whose specific expertise will facilitate achievement of program objectives. While a background in a specific disease state is often believed to be the prioritized prerequisite, other considerations may be of equal, or possibly greater, importance especially to earlier-stage companies. These include:
Despite the multiple benefits of involving a CMO early in a drug candidate’s development, companies frequently do not hire a CMO prior to filing an IND. Often it is because of the expense or the less than a full-time need. Instead, these companies often rely on KOL or SAB members as a substitute, advisors that may lack the relevant clinical experience or may not have sufficient time for thoughtful engagement. Prior to committing to a full-time hire, an appropriate functional bridge may be the fractional CMO. Accessing a senior-level CMO talent on a fractional level provides the company the multitude of benefits a CMO can offer it without many of the financial encumbrances of a permanent employee. Moreover, while indication-specific knowledge may be desired, the broad functional capabilities of an experienced CMO often outweigh an understanding of a particular disease state. The backgrounds of seasoned CMO talents include experiences across many disease states, indicative of their ability to acquire requisite indication insights rapidly. Far too frequently do we see early-stage companies select a preclinical pathway for the wrong drug candidate targeting the wrong indication, inevitably leading to increased costs and delayed program advances, much of which can be avoided with input from an experienced Chief Medical Officer (CMO) executive. To that end I wanted to reach out to highlight our creation of the BJC Capital Advisors’ CMO executive network and underscore the benefit, especially for companies in preclinical development, of accessing an experienced CMO talent to align preclinical programs with your anticipated clinical development strategy.
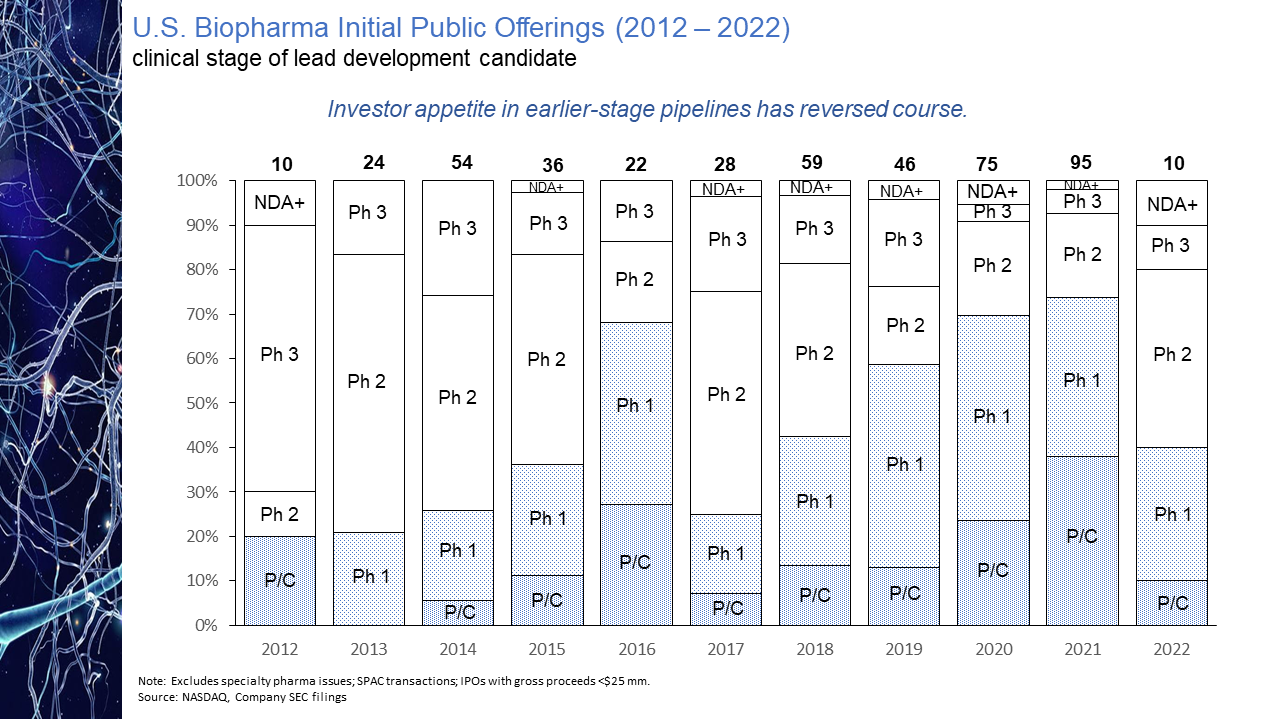
We have assembled our CMO network with experienced industry executives whose background typically combines exposures to both large pharmaceutical and smaller biotechnology companies. This diverse range of experiences provides our CMOs with an understanding of big company culture and expectations as well as an appreciation of the constraints small companies often face. We find this blend of insights maximizes the value our CMOs bring to client engagements. Executive talent can be accessed on either a fractional or interim basis, for as little as a few hours a month, with engagements structured to best accommodate company budgets. Accessing a CMO in this manner provides a functional solution for companies where the significant expense of a full-time hire is not justified. I imagine many of these perspectives may resonate with you. If so, we encourage you to please reach out to learn more about our CMO executive network and how our senior-level talent can benefit your development initiatives. 5/17/2023 The Changing Profile of Biopharma IPOs
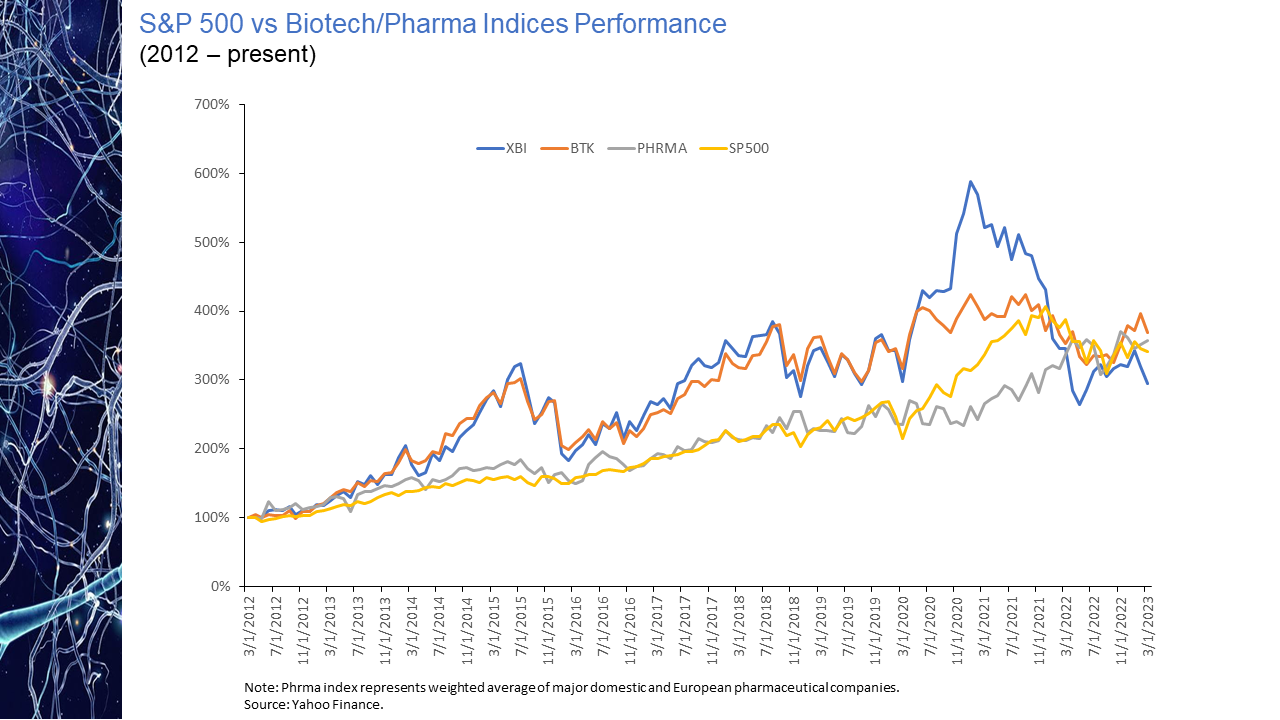
We are pleased to announce that last week we received notification from FINRA that our application for membership has been approved. Approval of the application, the culmination of a nearly ten-month process, formally designates the firm as a registered broker/dealer allowing us to participate in regulated securities transactions. FINRA membership extends the services we are able to provide earlier-stage life science companies to include private equity placements and transaction advisory services, including licensing, strategic partnerships and alliances, and mergers & acquisitions engagements, where we participate on both buy-side and sell-side engagements. These capabilities build upon decades of prior investment banking, strategy consulting and corporate management experience. Differentiating our transaction business are a range of complementary services that tailored primarily to the needs of emerging stage biopharmaceutical companies, including a chief medical officer (CMO) and chief business officer (CBO) executive network that provides access to distinguished senior-level talent on an interim or fractional basis and our IPO preparation services, where we work closely with company management to draft a compelling and thoughtful business section for S-1, F-1 and certain S-4 filings. We believe the seamless integration of this suite of capabilities addresses needs central to our clients’ success. member FINRA/SIPC The ongoing shift over the last decade towards biopharma as the primary originator of industry innovation, and the disproportionate value it generated, is perhaps best reflected in the market performance of the biopharma sector when compared to that of traditional pharmaceutical companies. As is noted in the chart presented below, over the last decade, the cumulative advance of biopharma, in particular the increase in the XBI index of earlier-stage biopharma companies, far outpaced the gains achieved by the traditional pharmaceutical industry. Remarkably, the spread in cumulative market appreciation between the XBI and traditional pharma approached an astounding 300% at its peak in early 2021. That contrast in market appreciation, achieved over a nearly ten-year period, quickly vanished in the year that followed. The perception of R&D as a key valuation driver during a time of relatively inexpensive money, appears to have quickly reversed itself, with the cumulative gains of a decade evaporating virtually overnight. Perhaps in anticipation of the higher interest rate environment that we now find ourselves in, sentiment began to shift even before the first interest rate hike. This valuation reset has reduced the aggregate returns of the XBI to below those of traditional pharma for the first time in ten+ years. While the implications of that reset are likely to reverberate until further economic clarity is achieved, interest rate stability may usher in renewed sector advance.
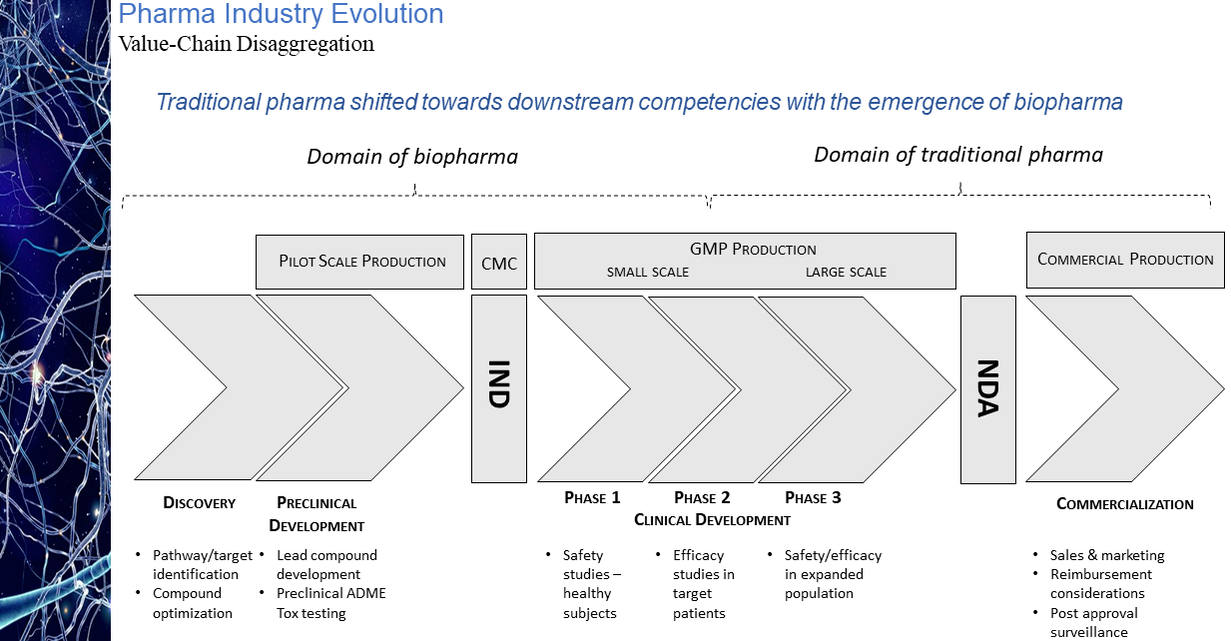
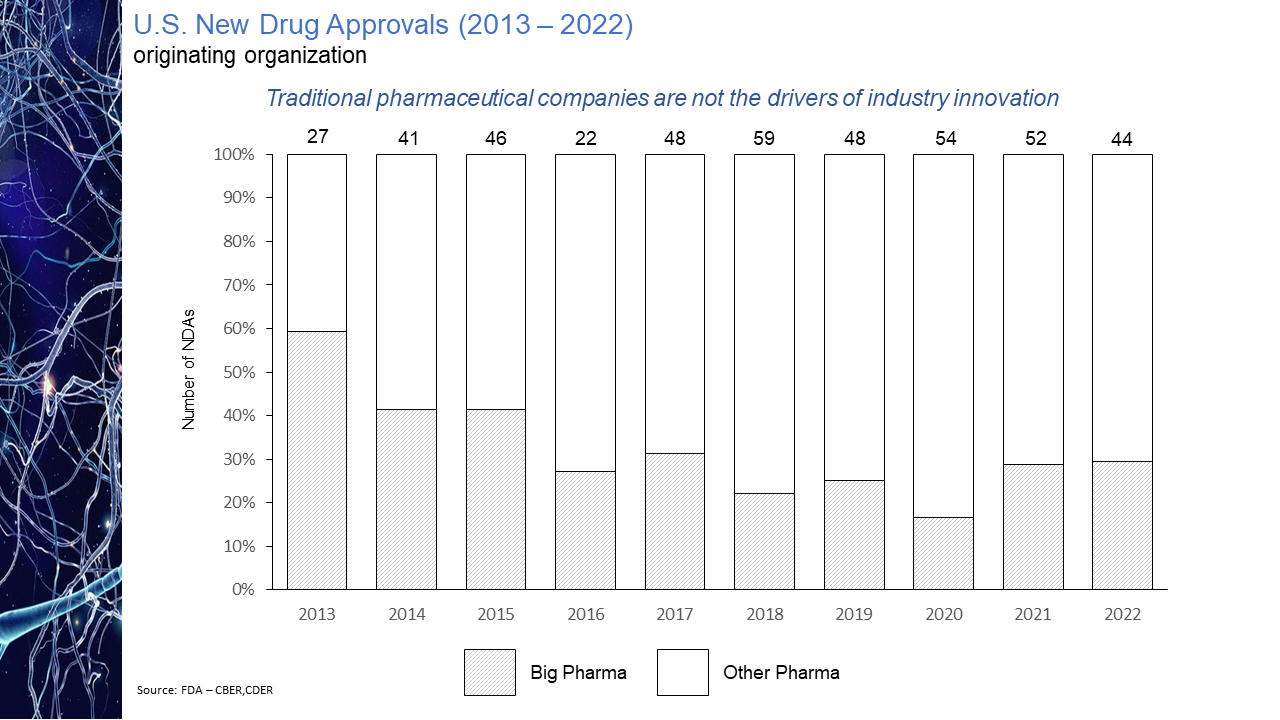
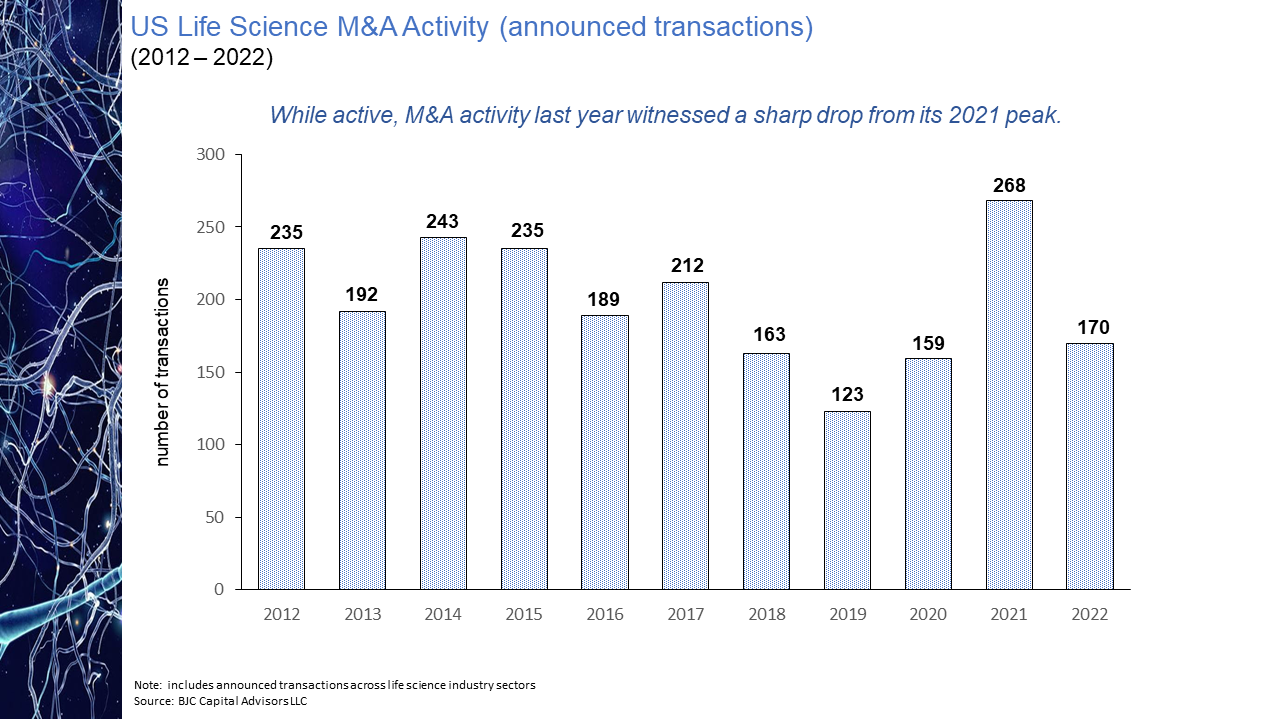
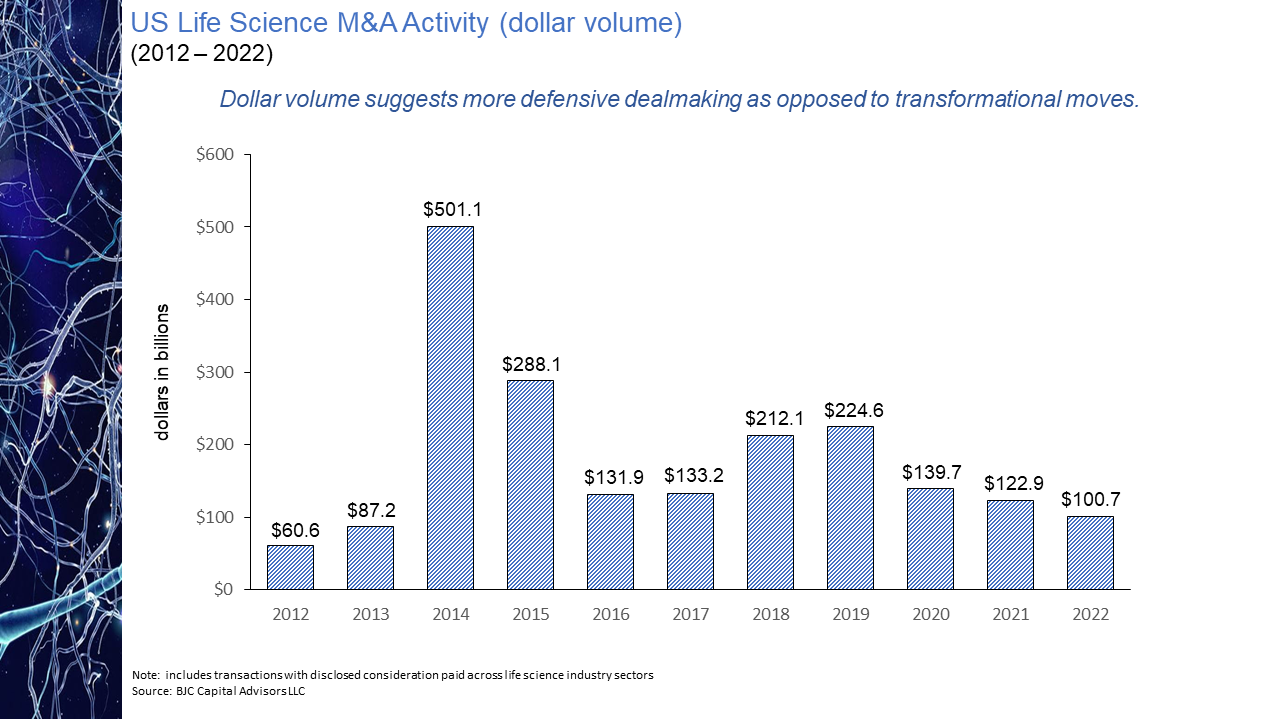
The evolution of the pharmaceutical industry has witnessed the continued disaggregation of the industry value chain. This disaggregation has resulted in larger, more established companies increasingly focused on downstream competencies in such areas as regulatory affairs and product commercialization with earlier-stage sector participants asserting themselves as the primary engines of industry innovation. As a result, today’s biopharmaceutical industry may arguably be considered largely an outsourced R&D function and feeder system for the commercial infrastructure of big pharma. While the migration of the industry towards this functional segregation is not a new phenomenon, what is striking is the degree of the shift. As is illustrated in the chart presented below, as recently as ten years ago some 60% of novel drug approvals were tied to companies whose origins could be traced to the traditional pharmaceutical industry. Within the last handful of years, however, that percentage has dropped to as low as 20%. Even this percentage may be an overstatement of the actual figure after factoring in the acquisition appetite of big pharma for its smaller biotech peers. The implications of this shift on market performance, a topic to be explored in an upcoming blog post, is notable. The IPO torrent of 2020 and 2021, during which time some 170 new issues came to market came to a screeching halt in 2022. Only 11 IPOs of any real size priced in 2022, four of them in the first two months of the year and prior to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. That dearth in IPO activity has continued into 2023 with only two meaningful new issues, Structure Therapeutics and Mineralys Therapeutics, coming to market. Even if the economic uncertainties that have clouded the market picture were to somehow resolve themselves, it seems unlikely that investors will regain enthusiasm for the sector any time soon with the XBI down more than 50% from its February 2021 high water mark. With biopharma currently out of public market favor and with valuations substantially discounted relative to their 2021 levels, many industry participants believe the pace of mergers and acquisition activity is bound to accelerate, as strategic acquirors step in to bolster pipelines with promising clinical candidates at depressed prices. Evidence does not seem to support this position. As seen in the chart below, measured by number of announced life science transactions, while M&A activity did not follow IPOs off a cliff last year, the level of activity did pull back quite considerably, down nearly 37% year-over-year. This decline in dealmaking suggests that despite what may be considered a buyer’s market, the appetite of large pharmaceutical companies to expand their cash burn rates is limited especially for assets whose payback is often many years off, if then. Not surprisingly and not unlike other industry sectors, M&A interest in times of economic uncertainty in the pharma industry appears to be more narrowly focused on smaller, complementary “bolt-on” acquisitions rather than bold, transformational moves. This deal bias is perhaps best reflected in the aggregate dollar volume of transactions announced in 2022, the $101 billion total the lowest in a decade while the number of announced transactions displayed a slight uptick over the years immediately pre-pandemic. The 35% decline from 2021 in the number of billion-dollar deals is further indication of this more conservative M&A mindset. Hence while industry lore may have us believe interest in strategic M&A increased with public market downturns, actual transaction data is evidence of quite the opposite.
|
About the AuthorBen Conway is a long-tenured investment banker with a primary focus on the biopharmaceutical sector. In addition to investment banking, his experience includes positions in large pharma as well as with smaller emerging biotech platforms. Archives
February 2024
|
BJC Capital Advisors LLC
Boston, Massachusetts
(617) 834-8482
Boston, Massachusetts
(617) 834-8482



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed